Package: gtk
Class gtk:file-chooser-dialog
Superclassesgtk:dialog, gtk:window, gtk:widget, gobject:initially-unowned, gtk:accessible, gtk:buildable, gtk:constraint-target, gtk:native, gtk:root, gtk:shortcut-manager, gtk:file-chooser, gobject:object, common-lisp:standard-object, common-lisp:t Documented Subclasses
None
Direct Slots
None
Details The gtk:file-chooser-dialog widget is a dialog suitable for use
with "File/Open" or "File/Save as" commands. This widget works by putting a gtk:file-chooser-widget widget inside a gtk:dialog widget. It exposes the gtk:file-chooser interface, so you can use all of the gtk:file-chooser functions on the file chooser dialog as well as those for the gtk:dialog widget. 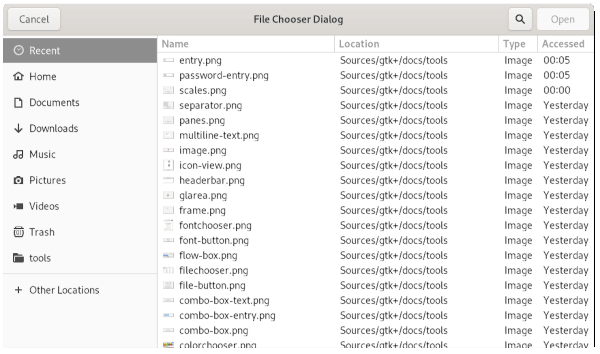 Figure: GtkFileChooserDialog Note that the gtk:file-chooser-dialog widget does not have any methods of its own. Instead, you should use the functions that work on a gtk:file-chooser interface. If you want to integrate well with the platform you should use the gtk:file-chooser-native API, which will use a platform-specific dialog if available and fall back to the gtk:file-chooser-dialog widget otherwise. Setting up a file chooser dialog
Response Codes
(let ((dialog (gtk:file-chooser-dialog-new "Open File"
parent-window
:open
"Cancel" :cancel
"Open" :accept)))
... )
This will create buttons for "Cancel" and "Open" that identifiers from the gtk:response-type enumeration. For most dialogs you can use your
own custom response codes rather than the ones in the gtk:response-type enumeration, but the gtk:file-chooser-dialog
widget assumes that its "accept"-type action, for example, an "Open" or
"Save" button, will have one of the following response codes: :accept :ok :yes :applyThis is because the gtk:file-chooser-dialog widget must intercept responses and switch to folders if appropriate, rather than letting the dialog terminate - the implementation uses these known response codes to know which responses can be blocked if appropriate. To summarize, make sure you use a predefined response code when you use the gtk:file-chooser-dialog widget to ensure proper operation. Examples
(defun create-file-chooser-dialog-open (window)
(let ((dialog (gtk:file-chooser-dialog-new "Open File"
window
:open
"Cancel" :cancel
"Open" :accept)))
(if (eq :accept (gtk:dialog-run dialog))
(let ((filename (gtk:file-chooser-filename dialog)))
...
))
(gtk:window-destroy dialog)))
To use a dialog for saving, you can use this:
(defun create-file-chooser-dialog-save (window filename)
(let ((dialog (gtk:file-chooser-dialog-new "Save File"
window
:save
"Cancel" :cancel
"Save" :accept)))
(setf (gtk:file-chooser-do-overwrite-confirmation dialog) t)
(if filename
(setf (gtk:file-chooser-filename dialog) filename)
(setf (gtk:file-chooser-current-name dialog) "Untitled document"))
(if (eq :accept (gtk:dialog-run dialog))
(let ((filename (gtk:file-chooser-filename dialog)))
...
))
(gtk:window-destroy dialog))) CSS nodesWarning | Returned byInherited Slot Access FunctionsSee also |
2025-09-21